- 1 Understanding the Operating Environment and Stress Factors
- 2 Abrasion-Induced Failures and Wear Protection Strategies
- 3 Chemical Degradation Mechanisms and Material Compatibility
- 4 Comparative Analysis of Common Failure Modes and Detection Methods
- 5 Preventative Maintenance Programs and Inspection Protocols
- 6 Installation Best Practices to Minimize Failure Risks
- 7 Emergency Response Planning for Hose Failure Scenarios
- 8 FAQ
- 8.1 What is the typical service life for mining dewatering hoses?
- 8.2 How can I determine the appropriate hose specifications for my mining application?
- 8.3 What are the most effective methods for inspecting dewatering hoses?
- 8.4 Are there specific storage requirements for mining dewatering hoses?
- 8.5 What safety precautions should be implemented during hose replacement?
Special mining outer dewatering hoses represent critical infrastructure components in mining operations, responsible for transporting water, slurry, and other fluids from mining sites to external treatment or discharge locations. These hoses operate under exceptionally demanding conditions, facing abrasive materials, chemical exposure, extreme pressures, and environmental challenges that can lead to various failure modes. Understanding these failure mechanisms and implementing proactive preventative strategies is essential for maintaining operational continuity, ensuring safety, and optimizing the total cost of ownership in mining dewatering applications.
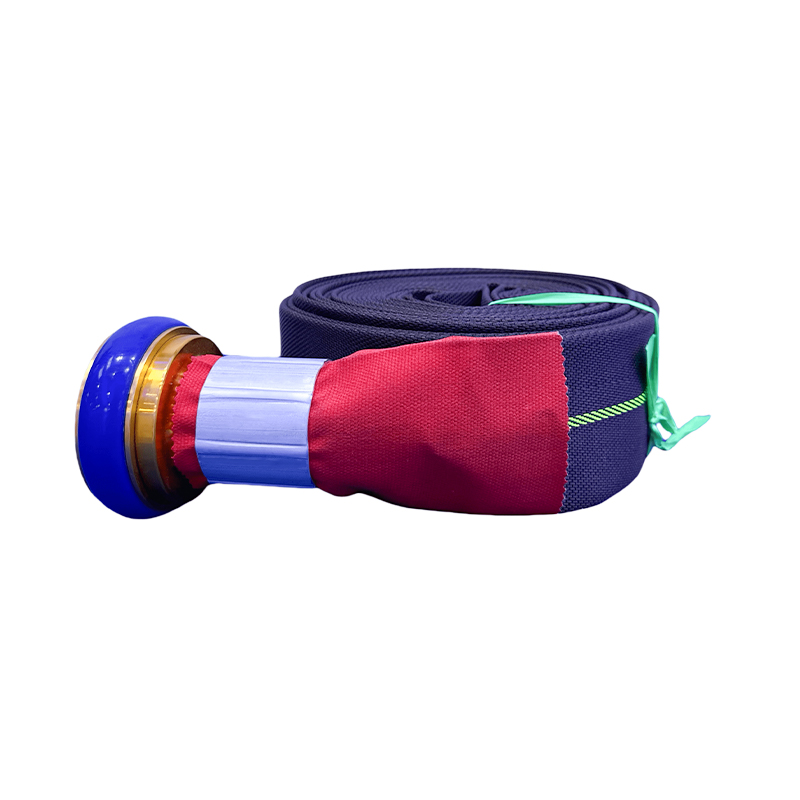
6-Inch Wear-Resistant Flat Hose With Storz Connector For Mining-Grade External Drainage
Understanding the Operating Environment and Stress Factors
The exceptional durability requirements for special mining outer dewatering hoses stem from the uniquely challenging environments in which they operate. Mining dewatering applications typically involve transporting abrasive slurries with varying particle sizes, chemical-laden water with potentially corrosive properties, and operating under significant pressure fluctuations and mechanical stresses. These combined factors create multiple potential failure points that must be addressed through proper hose selection, installation, and maintenance practices to ensure reliable long-term performance.
- Abrasive Particle Content: Solid particles in mining slurry create continuous wear on inner hose surfaces, particularly at bends and connection points.
- Chemical Compatibility Challenges: Acidic or alkaline mine water can degrade hose materials, compromising structural integrity over time.
- Pressure Cycling Effects: Frequent pressure fluctuations from pump operations cause material fatigue and potential delamination.
- Environmental Exposure Conditions: UV radiation, temperature extremes, and ozone exposure accelerate external degradation.
- Mechanical Stress Factors: Bending, twisting, and crushing forces during operation and handling create localized stress concentrations.
Abrasion-Induced Failures and Wear Protection Strategies
Abrasion represents the most common failure mechanism for special mining outer dewatering hoses, particularly when handling slurries with high solid content or sharp particulate matter. The continuous flow of abrasive materials gradually wears away the inner lining, eventually compromising the hose's pressure integrity and leading to leaks or catastrophic failure. Understanding wear patterns and implementing appropriate protection strategies can significantly extend service life while maintaining safe operation in demanding mining environments.
- Internal Wear Patterns: Concentrated erosion typically occurs at bends, connections, and areas of turbulent flow transition.
- Material Selection Considerations: Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) and specialized rubber compounds offer superior abrasion resistance.
- Reinforcement Protection: Embedded wear indicators and sacrificial layers provide visual warnings before critical failure occurs.
- Installation Optimization: Minimizing tight bends and ensuring proper alignment reduces localized wear acceleration.
- Flow Velocity Management: Maintaining optimal flow rates prevents excessive turbulence that accelerates abrasive wear.
Chemical Degradation Mechanisms and Material Compatibility
Chemical degradation poses significant challenges for special mining outer dewatering hoses, as mine water often contains various chemical compounds that can deteriorate hose materials over time. The degradation process typically involves chemical reactions between hose compounds and mine water constituents, leading to material softening, hardening, cracking, or swelling that compromises structural integrity. Understanding these chemical interactions enables proper material selection and preventative maintenance scheduling.
- pH-Related Deterioration: Both highly acidic (low pH) and alkaline (high pH) conditions can degrade different elastomer types.
- Oxidizing Agent Effects: Chemicals like chlorine or hydrogen peroxide accelerate aging through oxidation reactions.
- Hydrocarbon Swelling Issues: Oil or solvent contamination causes certain elastomers to swell, weakening reinforcement bonds.
- Temperature Acceleration: Elevated temperatures significantly increase chemical reaction rates, accelerating degradation.
- Additive Leaching: Chemical exposure can extract protective additives from hose materials, reducing flexibility and crack resistance.
Comparative Analysis of Common Failure Modes and Detection Methods
Different failure modes for special mining outer dewatering hoses present distinct characteristics, progression rates, and detection challenges. Early identification of specific failure types enables timely intervention before catastrophic incidents occur. The table below compares the most prevalent failure modes, their typical causes, observable symptoms, and recommended detection approaches to support effective preventative maintenance programs:
| Failure Mode | Primary Causes | Observable Symptoms | Detection Methods | Typical Progression Rate |
| Abrasion Wear | High solids content, sharp particles | Thinning walls, localized wear patterns | Ultrasonic thickness testing, visual inspection | Gradual (months to years) |
| Chemical Degradation | pH extremes, oxidizing chemicals | Cracking, swelling, hardness changes | Material sampling, durometer testing | Moderate (weeks to months) |
| Pressure Fatigue | Pressure cycling, water hammer | Bulging, reinforcement separation | Visual inspection, pressure decay testing | Cyclical (dependent on cycles) |
| UV/Ozone Damage | Sunlight exposure, atmospheric ozone | Surface cracking, discoloration | Visual inspection, flexibility testing | Slow (years in direct sun) |
| Mechanical Damage | Crushing, kinking, impact | Deformation, cuts, punctures | Visual inspection, pressure testing | Instantaneous or progressive |
This comparative analysis provides a foundation for developing targeted inspection protocols that address the specific failure risks present in each mining dewatering application.
Preventative Maintenance Programs and Inspection Protocols
Implementing structured preventative maintenance programs represents the most effective strategy for maximizing the service life of special mining outer dewatering hoses and preventing unexpected failures. A comprehensive maintenance approach combines regular inspections, performance monitoring, and proactive replacement based on established wear indicators rather than waiting for visible damage or performance degradation. Well-designed maintenance protocols significantly reduce downtime, repair costs, and safety risks associated with hose failures in mining operations.
- Scheduled Inspection Intervals: Establish regular inspection frequencies based on operating hours, material transported, and environmental conditions.
- Documentation and Tracking Systems: Maintain detailed records for each hose section, including installation date, service history, and repair documentation.
- Performance Monitoring Parameters: Track flow rates, pressure drops, and visual indicators to identify developing issues before failure occurs.
- Preventative Replacement Criteria: Establish clear replacement thresholds based on measurable parameters like wall thickness reduction.
- Spare Parts Inventory Management: Maintain appropriate inventory levels to minimize downtime when replacement becomes necessary.
Installation Best Practices to Minimize Failure Risks
Proper installation techniques significantly influence the performance longevity and failure resistance of special mining outer dewatering hoses. Incorrect installation creates immediate stress points and accelerated wear patterns that substantially reduce service life, regardless of hose quality or maintenance practices. Following manufacturer-recommended installation procedures and industry best practices ensures optimal performance while minimizing premature failure risks in demanding mining environments.
- Bend Radius Compliance: Maintain minimum bend radii specified by manufacturers to prevent kinking and uneven wear patterns.
- Proper Support and Suspension: Implement adequate support systems to prevent excessive sagging, abrasion against surfaces, and stress concentrations.
- Connection and Coupling Installation: Ensure proper fitting selection, installation torque, and alignment to prevent leakage and connection failures.
- Environmental Protection Measures: Implement shielding from UV exposure, extreme temperatures, and potential impact damage where applicable.
- Pressure Testing Protocols: Conduct comprehensive pressure testing after installation to identify manufacturing defects or installation issues.
Emergency Response Planning for Hose Failure Scenarios
Despite comprehensive preventative measures, emergency response planning for potential special mining outer dewatering hose failures remains essential for minimizing operational disruption, environmental impact, and safety risks. A well-developed emergency response plan establishes clear procedures for rapid containment, isolation, and repair of failed hose sections, ensuring coordinated action during high-stress situations. Regular drills and equipment preparation further enhance response effectiveness when actual failures occur.
- Containment Strategy Development: Establish procedures and equipment for containing spilled fluids to prevent environmental contamination.
- Isolation Protocol Implementation: Design systems with strategically placed isolation valves to minimize fluid loss during failure events.
- Emergency Repair Kits: Maintain readily accessible repair materials, tools, and personal protective equipment at strategic locations.
- Communication Procedures: Establish clear communication protocols to coordinate response efforts across different operational areas.
- Post-Failure Analysis Processes: Implement systematic failure analysis to identify root causes and prevent recurrence.
FAQ
What is the typical service life for mining dewatering hoses?
The service life of special mining outer dewatering hoses varies significantly based on multiple factors including operating conditions, material composition, and maintenance practices. Under typical mining conditions with moderate abrasion and chemical exposure, high-quality hoses generally provide 2-5 years of reliable service. However, in extremely abrasive applications with high solid content, service life may be reduced to 6-18 months without proper rotation and maintenance. Regular inspection and adherence to manufacturer recommendations are crucial for maximizing hose longevity while ensuring safe operation.
How can I determine the appropriate hose specifications for my mining application?
Selecting the correct mining dewatering hose specifications requires careful analysis of multiple operational parameters. Key considerations include maximum operating pressure with appropriate safety factors, fluid composition (pH, chemical content, abrasiveness), temperature ranges, flow rate requirements, and environmental conditions. Additionally, practical factors like installation geometry, connection compatibility, and handling requirements influence specification decisions. Consulting with technical specialists and reviewing application case studies with similar operating conditions provides valuable guidance for optimal hose selection.
What are the most effective methods for inspecting dewatering hoses?
Effective inspection of special mining outer dewatering hoses employs a multi-method approach combining visual examination, non-destructive testing, and performance monitoring. Visual inspections should focus on identifying surface cracks, abrasion patterns, bulges, and connection integrity. Ultrasonic thickness testing provides quantitative data on wall thickness reduction from abrasion. Pressure decay tests help identify developing leaks or reinforcement damage. Additionally, monitoring operational parameters like pressure fluctuations and flow restrictions can indicate internal wear before visible external symptoms appear.
Are there specific storage requirements for mining dewatering hoses?
Proper storage practices significantly impact the performance and longevity of special mining outer dewatering hoses. Hoses should be stored in cool, dry environments away from direct sunlight, ozone sources, and extreme temperatures. They should be laid flat or suspended in straight configurations rather than tightly coiled to prevent permanent deformation. Additionally, hoses should be protected from rodent damage, chemical contamination, and heavy objects that could cause crushing. Following manufacturer-specific storage recommendations preserves material properties until installation and commissioning.
What safety precautions should be implemented during hose replacement?
Replacing special mining outer dewatering hoses requires implementation of comprehensive safety protocols to protect personnel and equipment. Essential precautions include complete system depressurization and verification, proper lockout/tagout procedures, use of appropriate personal protective equipment, securing hose sections to prevent uncontrolled movement, and ensuring adequate ventilation when working in confined spaces. Additionally, emergency response equipment should be readily accessible, and multiple personnel should be present during critical replacement operations to address potential hazards effectively.


 en
en
 عربى
عربى