Foundational Principles for Sizing Your Layflat Hose
Understanding the Critical Role of Diameter and Pressure
Selecting the correct PVC layflat hose is paramount for operational safety and efficiency. This process hinges on two core parameters: the hose's diameter and its pressure ratings. A professional approach requires careful analysis of the system's requirements to prevent inefficiency and safety hazards.
- Diameter and Flow Rate: The hose's diameter directly dictates the volume of fluid it can transfer, also known as the flow rate. A larger diameter is essential for high-volume applications.
- Pressure Ratings: Every hose has a Working Pressure (WP) for safe continuous use and a Burst Pressure (BP), which is the point of catastrophic failure.
- Specialized Hoses: A heavy duty pvc layflat hose is engineered with reinforced polyester yarn to withstand significantly higher pressures and abrasions than a standard hose.
- Professional Selection: A professional balances flow rate, pressure, and environmental factors to ensure the hose's specifications align perfectly with the application's demands.
The Impact of Hose Length and Elevation on Performance
Beyond diameter and pressure, two critical factors influencing system performance are hose length and elevation. These elements contribute to pressure loss, or head loss, which can significantly reduce the efficiency of fluid transfer.
- Frictional Loss: Pressure is lost as fluid moves against the hose's inner wall. This loss increases with hose length and flow velocity. Using a larger-diameter hose for long distances is a strategic way to reduce this friction.
- Elevation Loss: Pumping fluid uphill requires energy to overcome gravity. For every foot of vertical lift, pressure drops by approximately 0.433 PSI.
- Comprehensive Calculation: Professionals meticulously calculate both horizontal and vertical distances to ensure the pump's head capacity is sufficient to meet the demands of the entire system.
Matching Hose Type to Specific Application Needs
The distinction between different hose types is crucial for both safety and performance. Choosing the right hose means matching its material and construction to the specific task.
- Type Comparison: A layflat fire hose vs pvc layflat hose highlights key differences in construction. Fire hoses are built for extreme, high-pressure environments, while PVC hoses are ideal for general-purpose, medium-pressure tasks like irrigation and dewatering.
- Irrigation Use: A pvc layflat hose for irrigation is designed for flexibility and portability. Its size must be chosen to ensure an even flow rate across the field, preventing pressure drops that lead to uneven watering.
- Pumping Use: A pvc layflat hose for water pump applications must be perfectly sized to the pump's discharge outlet. Mismatching can cause back pressure, pump strain, and premature wear.
Practical Applications and Sizing Considerations
Choosing the Right Hose for Agricultural and Industrial Use
Agricultural and industrial applications rely on precise hose selection for efficient operation. A professional selects a hose diameter that ensures a consistent flow rate, minimizing energy waste and preventing system failures.
- For Irrigation: Sizing a pvc layflat hose for irrigation is a key step. Under-sizing can lead to significant friction loss, causing pressure drops and uneven water distribution. A 3" or 4" diameter hose is often preferred for large fields.
- For Industrial Use: In industrial settings, a heavy duty pvc layflat hose is often required for abrasive liquids or high-pressure transfer. The hose diameter should always be equal to or larger than the pump's discharge outlet to ensure maximum efficiency.
- Professional Approach: This meticulous approach guarantees reliable fluid transfer without system failures or operational inefficiencies.
Sizing Hoses for Pumping and Water Transfer
The efficiency of any water transfer system hinges on the correct sizing of the pvc layflat hose for water pump. A common and critical error is a mismatch between the pump's outlet and the hose's diameter.
- The Bottleneck Effect: Undersizing the hose creates a bottleneck, forcing the pump to work against high back pressure. This leads to increased energy consumption, pump overheating, and potential cavitation.
- The Professional Rule: Always match the hose diameter to the pump's discharge outlet. For long distances, using a larger hose can strategically reduce friction loss and allow the pump to operate more efficiently.
- System Integrity: The hose is not merely an accessory; it is an integral component of the pumping system. Proper sizing ensures the pump operates within its optimal parameters, maximizing its lifespan and reliability.
| Pump Outlet Diameter | Hose Diameter (Matched) | Friction Loss (per 100 ft) | System Efficiency |
| 3 inches | 3 inches | ~5-10 PSI | High - Pump operates within optimal parameters, minimal head loss. |
| 3 inches | 2 inches (Undersized) | ~30-40 PSI | Low - High back pressure, increased pump strain, risk of cavitation. |
| 4 inches | 4 inches | ~3-7 PSI | Very High - Optimal flow with minimal pressure drop, ideal for long runs. |
The Importance of Compatible Fittings and Connections
The integrity of a layflat hose system is determined by the quality of its connections. Selecting the right layflat discharge hose fittings is as critical as choosing the hose itself.
- Matching Diameter: The fitting's diameter must precisely match the hose's internal diameter to ensure a secure, leak-proof seal.
- Common Types: Professionals use camlock fittings for their quick, tool-free connection, quick connect fittings for frequent setup, and hose clamps for secure, semi-permanent attachments.
- Routine Maintenance: Regular inspection of fittings and gaskets is crucial for preventing leaks and system failure. The choice of fitting material should also be based on the application and environment.
- System Integrity: A well-designed system ensures that every component, from the hose to the fittings, works in perfect harmony to guarantee safety and reliability.
| Fitting Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best For |
| Camlock (Cam and Groove) | Quick connection, tool-free, versatile materials, secure seal. | Gaskets can wear out, can be heavy in larger sizes, not ideal for very high pressures. | General purpose water transfer, agriculture, industrial applications. |
| Quick Connect | Very fast deployment, lightweight, easy to use, ideal for temporary setups. | May not handle extremely high pressures, more prone to damage if dropped. | Residential dewatering, construction sites, applications requiring frequent setup and tear-down. |
| Hose Clamps | Inexpensive, strong hold, simple design, can be used on various connections. | Requires a tool to tighten, can damage hose if overtightened, not for quick connections. | Permanent or semi-permanent installations, securing hose to a pump outlet. |
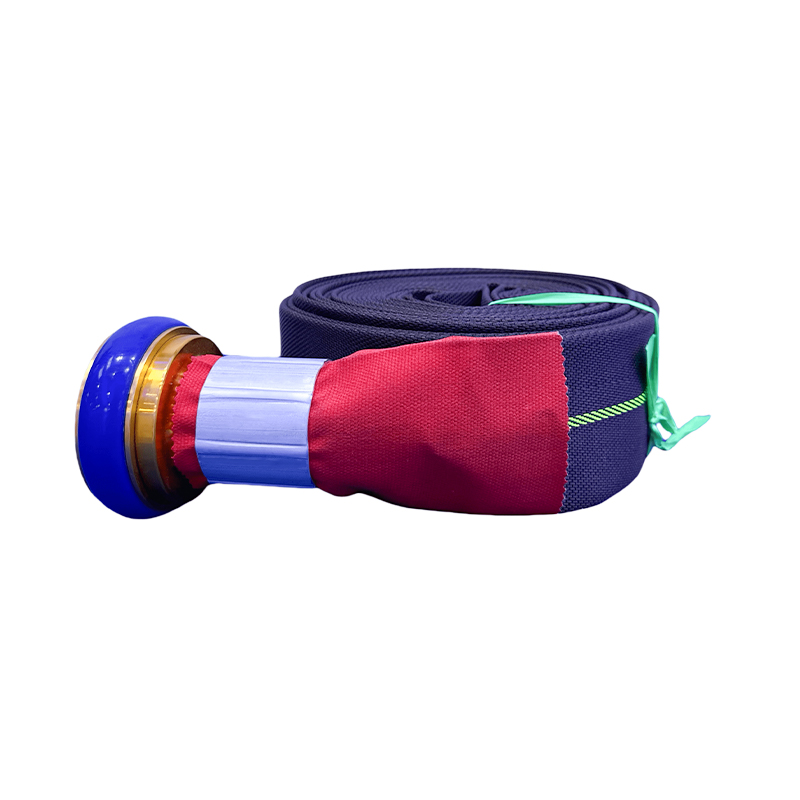
1" - 6" Canvas Hose PVC Lined Layflat Hose For Fire Extinguishing/Agricultural Irrigation
A Detailed Look at Common Layflat Hose Diameters
Understanding the Standard Range
Standard PVC layflat hoses are available in a common range of internal diameters, each offering a balance of flow capacity, pressure handling, and physical manageability for different applications. A professional understands this hierarchy of sizes, enabling them to quickly select the most appropriate hose.
- 1.5" and 2": Ideal for light-duty tasks like residential dewatering, garden irrigation, and small pumps due to their portability and ease of handling.
- 3" and 4": These are industry workhorses, widely used in agriculture for irrigation and on construction sites. They offer a significant increase in flow rate for medium to large-scale projects.
- 6" and Larger: Used for the most demanding applications, such as high-volume industrial pumping or mining, due to their superior flow capabilities.
- Strategic Choice: The selection of a heavy duty pvc layflat hose is a strategic one, providing greater durability and pressure resistance for harsh environments.
| Hose Diameter (inches) | Typical Flow Rate (GPM) | Best Suited Applications |
| 1.5" | Up to 100 GPM | Light-duty water transfer, small pumps, garden irrigation, residential dewatering. |
| 2" | Up to 150 GPM | Medium-duty water transfer, swimming pool drainage, small construction sites. |
| 3" | Up to 350 GPM | Agricultural irrigation, larger dewatering projects, municipal water transfer. |
| 4" | Up to 600 GPM | Large-scale agricultural and industrial water transfer, flood control. |
| 6" | Up to 1,500 GPM | Very high-volume industrial pumping, emergency water supply, mining. |


 en
en
 عربى
عربى