- 1 What is a Mining Outer Dewatering Hose?
- 2
- 3 Key Features of a High-Performance Mining Dewatering Hose
- 4 Top 5 Benefits of Using a Specialized Mining Dewatering Hose
- 5 Selecting the Right Heavy-Duty Dewatering Hose for Your Mine
- 6 Common Applications of Abrasion-Resistant Slurry Hoses in Mining
- 7 Maintenance and Best Practices for Long-Lasting Dewatering Hose Performance
- 8 FAQ
- 8.1 What is the difference between a mining dewatering hose and a standard water hose?
- 8.2 How long does a typical abrasion-resistant slurry hose last?
- 8.3 Can these hoses be used for both suction and discharge?
- 8.4 What are the signs that my dewatering hose needs replacing?
- 8.5 How do I choose between different rubber compounds for the outer cover?
The mining industry relies on robust and efficient equipment to handle its demanding dewatering tasks. At the heart of many of these operations is the specialized mining outer dewatering hose, a critical component designed to transport water, slurry, and other fluids away from excavation sites. Unlike standard hoses, these are engineered to withstand the harsh conditions of mining environments, including abrasion, high pressure, and extreme weather. Selecting the right hose is not just a matter of convenience; it directly impacts operational efficiency, safety, and bottom-line costs. This article delves deep into the unique features, material composition, and significant benefits that these specialized hoses bring to the mining sector, providing a comprehensive guide for industry professionals.
What is a Mining Outer Dewatering Hose?
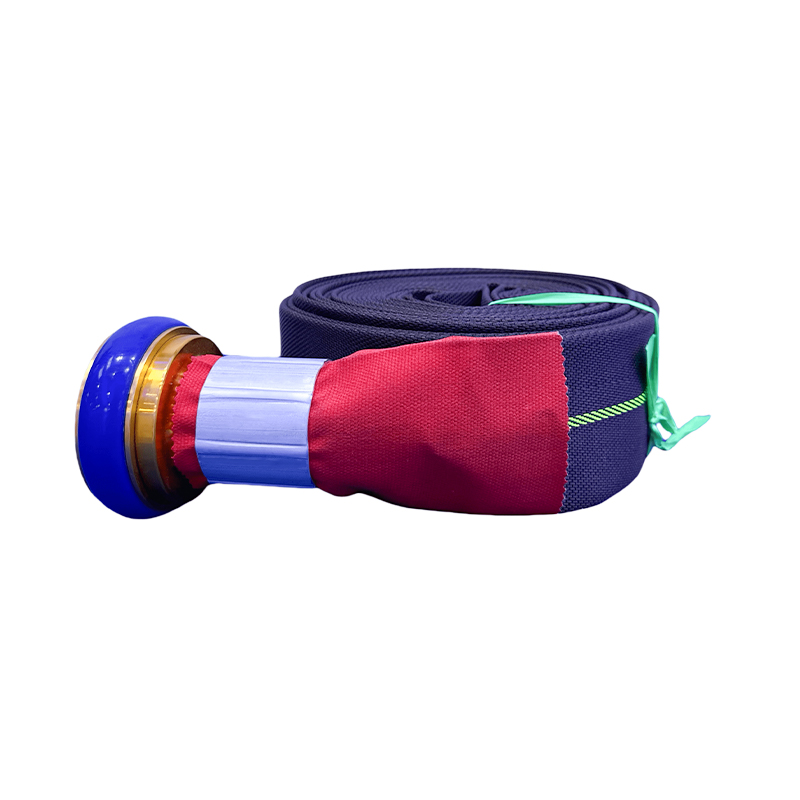
A mining outer dewatering hose is a heavy-duty, flexible pipeline specifically constructed for the large-scale removal of water from mining operations. These hoses are a far cry from ordinary garden hoses; they are engineered with multiple layers of synthetic fabric, steel wire reinforcement, and abrasion-resistant rubber compounds to create a formidable tube capable of handling immense stress. The primary function is to dewater pits, move slurry, and manage tailings, ensuring that mining activities can proceed without water obstruction. Their design prioritizes not only strength and durability but also flexibility to navigate the often uneven and challenging terrain of a mine site, making them an indispensable tool for continuous operation.
- Core Function: Designed for high-volume water and slurry transfer in open-pit and underground mines.
- Construction: Typically features a multi-layer design with an inner tube, multiple textile and steel cord reinforcements, and a rugged outer cover.
- Pressure Handling: Built to withstand high working pressures and vacuum conditions without collapsing or bursting.
- Dimensional Range: Available in large diameters, often ranging from 4 inches up to 20 inches or more, to facilitate massive flow rates.
8-Inch Mining Pressure-Resistant External Drainage Flat Hose Pipe With Storz Connectors
Key Features of a High-Performance Mining Dewatering Hose
The exceptional performance of a premium mining dewatering hose stems from a combination of meticulously engineered features. Each element, from the inner tube to the outer cover, is selected and designed to combat a specific challenge present in the mining environment. The inner layer must be smooth to minimize friction and abrasion from solid particles, while the reinforcement layers provide the necessary tensile strength to handle high pressure. The outer cover acts as the first line of defense against external damage, resisting cuts, tears, ozone, and weather. Understanding these features is key to selecting a hose that will deliver reliability and a long service life, reducing downtime and replacement frequency.
- Abrasion-Resistant Inner Tube: Made from compounds like SBR or NBR rubber to resist wear from suspended solids and slurry.
- High-Tensile Reinforcement: Layers of high-strength synthetic fabric and steel wire cord provide exceptional burst pressure resistance and prevent kinking.
- Weather & Ozone Resistant Cover: The outer cover is treated to resist degradation from sunlight, ozone, and extreme temperatures, preventing cracking.
- Flexibility: Despite its strength, a good hose maintains flexibility for easier handling and deployment across rocky terrain.
Material Composition and Durability
The longevity and resilience of a mining dewatering hose are directly dictated by its material composition. Manufacturers use a blend of synthetic rubbers and polymers, each chosen for its specific properties. The inner tube is often a mix of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) for its excellent abrasion resistance or Nitrile Butadiene Rubber (NBR) for better oil resistance if needed. The reinforcement is a critical area, where high-tensile textile piles and spiral-wound steel wire work in tandem to provide structural integrity. Finally, the outer cover is typically made from a tough rubber compound, often chloroprene or EPDM, which is resistant to environmental damage. This sophisticated material science is what allows these hoses to perform reliably in the world's toughest mining applications.
- Inner Tube Compounds: SBR (for general abrasion), NBR (for oil-based fluids), and sometimes special polyurethane blends.
- Reinforcement Materials: High-tensile polyester or nylon fabric, combined with high-carbon steel wire for spiral reinforcement.
- Outer Cover Compounds: Chloroprene (Neoprene) for a balance of weather, oil, and flame resistance, or EPDM for superior ozone and weather resistance.
- Durability Factor: The synergy between these materials results in a hose that resists abrasion, maintains flexibility under load, and withstands prolonged outdoor storage.
Pressure and Suction Capabilities
Mining dewatering hoses are unique in that they must often perform dual roles: handling positive pressure when pumping water out and resisting collapse under suction when drawing water in. This requires a carefully balanced construction. The spiral steel wire reinforcement is the key component that provides the crush resistance needed for vacuum or suction duties, preventing the hose from collapsing. Simultaneously, this reinforcement, along with the textile layers, gives the hose its high pressure rating for discharge applications. This dual capability makes them incredibly versatile, often eliminating the need for separate suction and discharge lines and simplifying the setup on site.
- Working Pressure: Designed to handle high working pressures, commonly ranging from 150 to 300 PSI or more, depending on the diameter and construction.
- Vacuum (Suction) Rating: The steel spiral reinforcement allows it to withstand full vacuum conditions (up to -1 Bar / -14.7 PSI) without collapsing.
- Burst Pressure: The ultimate failure pressure is typically 4 to 6 times the working pressure, providing a significant safety factor.
- Application Versatility: This combination allows a single hose to be used for both suction and discharge, making it a cost-effective solution.
Top 5 Benefits of Using a Specialized Mining Dewatering Hose
Investing in a purpose-built mining outer dewatering hose yields a multitude of benefits that extend far beyond simple water transfer. These advantages translate into tangible operational improvements and cost savings. The primary benefit is unparalleled durability, which directly reduces the frequency of hose failures and the associated costs of replacement and downtime. Enhanced safety is another critical advantage, as a robust hose minimizes the risk of sudden bursts that could lead to injuries or flooding. Furthermore, their efficiency in moving large volumes of water quickly keeps projects on schedule and reduces the energy required for pumping, contributing to both productivity and sustainability goals.
- Extended Service Life: Superior abrasion and weather resistance mean fewer replacements, lowering the total cost of ownership.
- Enhanced Operational Safety: High burst pressure ratings and reliable construction prevent dangerous failures that could harm personnel or equipment.
- Improved Efficiency & Flow Rates: A smooth bore and large diameters minimize friction loss, allowing for faster dewatering and reduced pump fuel consumption.
- Versatility Across Applications: Suitable for a wide range of fluids, from clean water to abrasive slurries and tailings, across various mining sites.
- Reduced Maintenance Downtime: Their rugged design withstands harsh conditions, meaning less time spent on repairs and more time on productive work.
Selecting the Right Heavy-Duty Dewatering Hose for Your Mine
Choosing the correct heavy-duty dewatering hose is a critical decision that requires careful consideration of several application-specific factors. A mismatch can lead to premature failure, safety hazards, and inflated costs. The first step is to clearly define the fluid being transported—is it clean water, slurry with abrasive particles, or does it contain chemicals or oils? Next, the operating pressure and required flow rate will determine the necessary diameter and pressure rating. Environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures or constant exposure to sunlight, will influence the material choice for the outer cover. Finally, considering practical aspects like required length, coupling systems, and storage methods will ensure a seamless integration into your mining operation.
- Assess the Fluid Type: Determine the chemical compatibility and abrasiveness of the fluid to select the appropriate inner tube material (e.g., NBR for oils).
- Determine Pressure & Vacuum Requirements: Select a hose with a working pressure and vacuum rating that exceeds your maximum operating conditions.
- Evaluate Environmental Conditions: Choose an outer cover material resistant to UV, ozone, and temperature extremes if the hose will be stored or used outdoors long-term.
- Consider Hose Size & Flexibility: Balance the need for large diameter (for flow) with the practical need for flexibility and ease of handling on the terrain.
Understanding Diameter and Length Requirements
The diameter and length of a dewatering hose are not arbitrary choices; they are fundamental engineering parameters that directly impact system performance. The diameter primarily governs the flow rate and velocity of the fluid. A larger diameter allows for a higher volume of water to be moved at a lower velocity, which reduces friction loss and abrasive wear on the hose interior. Conversely, a hose that is too long will increase friction loss, requiring more pump power to achieve the desired flow. Therefore, selecting the optimal combination of diameter and length is a balancing act that aims to maximize flow efficiency while minimizing pressure drop and wear, ultimately leading to lower operational costs.
- Flow Rate vs. Diameter: Larger diameters (e.g., 12-inch) support higher flow rates with less pressure loss compared to smaller diameters (e.g., 6-inch).
- Friction Loss Consideration: Longer hoses increase friction loss, which must be compensated for by a more powerful pump, increasing fuel costs.
- Practical Handling: Extremely long sections can be cumbersome to handle; using multiple shorter hoses with couplings can improve maneuverability.
- System Design: Always consult pump performance curves and system design calculations to determine the ideal hose size and length for your specific setup.
| Hose Diameter (Inches) | Approx. Flow Rate (US GPM)* | Typical Application |
| 6" | 1,500 - 2,200 | Small pit dewatering, auxiliary lines |
| 8" | 2,800 - 4,000 | Medium-scale dewatering, slurry transfer |
| 10" | 4,400 - 6,500 | Large pit dewatering, tailings delivery |
| 12" | 6,500 - 9,500 | High-volume main discharge lines, dredging |
*Flow rates are approximate and depend on pressure and system design.
Common Applications of Abrasion-Resistant Slurry Hoses in Mining
The application of abrasion-resistant slurry hoses within the mining industry is vast and varied, covering nearly every process that involves moving mixtures of water and solid materials. Their primary role is in dewatering, where they are used to pump out rainwater or groundwater from excavation sites to allow for safe and dry working conditions. Beyond this, they are indispensable in the handling of tailings—the fine, abrasive waste material left over after ore processing. These hoses transport the tailings in slurry form to storage facilities. They are also used in dredging operations within settling ponds, in process water lines, and for transferring raw ore slurries from one processing stage to another, proving their versatility and critical importance.
- Open-Pit Mine Dewatering: Pumping out accumulated water from rainfall or groundwater incursion to maintain a dry work floor.
- Tailings Transport: Moving the highly abrasive slurry of waste rock and water from the processing plant to tailings dams or storage facilities.
- Dredging and Pond Cleaning: Used with dredgers to remove settled solids from sedimentation ponds or water reservoirs.
- Process Water Transfer: Circulating large volumes of water used in various mineral processing and extraction methods.
- ROM (Run-of-Mine) Ore Slurry Transfer: Transporting a mixture of raw ore and water to the initial processing stages like crushers or wash plants.
Maintenance and Best Practices for Long-Lasting Dewatering Hose Performance
Maximizing the service life of a costly mining dewatering hose requires a proactive approach to maintenance and adherence to operational best practices. Proper care begins with correct storage—hoses should be stored flat in a cool, dry, dark place away from ozone sources like electric motors. Before use, a thorough visual inspection for cuts, cracks, or exposed reinforcement is essential. During operation, it's crucial to avoid dragging the hose over sharp rocks or running equipment over it. After use, thoroughly flushing the hose to remove internal abrasive particles can significantly extend the life of the inner tube. Implementing a regular inspection and maintenance schedule is the most effective strategy for preventing unexpected failures and ensuring a strong return on investment.
- Proper Storage: Coil or store flat on a clean, flat surface. Avoid kinking and protect from direct sunlight, extreme heat, and cold.
- Pre-Use Inspection: Check the entire length for any signs of damage to the cover, reinforcement, or couplings.
- Correct Installation: Use proper lifting equipment to move large hoses. Avoid sharp bends below the minimum bend radius specified by the manufacturer.
- Post-Use Flushing: After pumping slurry, flush the hose with clean water to remove abrasive solids trapped inside.
- Coupling Integrity: Regularly inspect and maintain couplings and flanges to ensure a secure, leak-free connection that won't slip under pressure.
FAQ
What is the difference between a mining dewatering hose and a standard water hose?
The differences are profound and relate to construction, materials, and capability. A standard water hose is typically a single-layer PVC or lightweight rubber design meant for low-pressure residential use. In contrast, a mining outer dewatering hose is a heavy-duty, multi-layered engineering product. It features a thick, abrasion-resistant inner tube, multiple layers of high-tensile textile and steel wire reinforcement for high pressure and vacuum resistance, and a rugged, weather-proof outer cover. This construction allows it to handle abrasive slurries, resist crushing under suction, and endure the physical abuse of a mining environment, far exceeding the capabilities of any standard hose.
How long does a typical abrasion-resistant slurry hose last?
The service life of an abrasion-resistant slurry hose is not a fixed number; it varies significantly based on application conditions. Key factors include the abrasiveness and acidity of the slurry being pumped, the operating pressure and velocity, how often the hose is moved, and adherence to maintenance practices. In a highly abrasive tailings application with constant use, a hose might last 6 to 12 months. In a less severe dewatering application with intermittent use and proper care, the same hose could last for several years. The best way to maximize lifespan is to select the correct hose for the duty and follow rigorous maintenance and inspection routines.
Can these hoses be used for both suction and discharge?
Yes, absolutely. One of the defining features of a true mining dewatering hose is its ability to perform both suction and discharge duties. This dual functionality is made possible by the spiral steel wire reinforcement embedded in its wall. This steel spiral provides the structural rigidity needed to prevent the hose from collapsing under vacuum (suction) while also contributing to its high burst pressure rating for discharge. This eliminates the need for and cost of maintaining two separate hose inventories, making operations more efficient and versatile. Always confirm the manufacturer's specifications for maximum vacuum and pressure ratings before use.
What are the signs that my dewatering hose needs replacing?
Recognizing the end of a hose's service life is critical for preventing costly failures. Key visual signs include significant cracking or checking on the outer cover, which exposes the reinforcement to moisture and corrosion. Any visible steel wire reinforcement or textile fabric is a definitive sign that the hose requires immediate replacement. Other indicators include localized bulging or swelling of the hose body, which suggests internal reinforcement failure, and a noticeable increase in flexibility or "soft spots," which can precede a burst. Regularly monitoring for these signs during inspection cycles is a fundamental best practice for maintenance crews.
How do I choose between different rubber compounds for the outer cover?
Selecting the right outer cover compound depends on the environmental threats the hose will face. The two most common options are Neoprene (Chloroprene) and EPM/EPDM. Neoprene offers a excellent all-around balance, providing good resistance to abrasion, weather, ozone, oils, and flames. It is a versatile choice for most general mining applications. EPDM, on the other hand, offers superior resistance to ozone, weathering, and heat, but it is not resistant to oils. Therefore, EPDM is an ideal choice for applications where the hose will be stored outdoors for long periods or used in high-ozone environments, but only if oil resistance is not a requirement.


 en
en
 عربى
عربى