- 1 What is a Special Mining Outer Dewatering Hose?
- 2 Key Applications in the Mining Industry
- 3 How to Select the Right Dewatering Hose for Your Mine
- 4
- 5 FAQ
- 5.1 What is the difference between a dewatering hose and a standard water hose?
- 5.2 How often should a mining dewatering hose be inspected?
- 5.3 Can a mining dewatering hose handle acidic or chemical water?
- 5.4 What does the "outer" refer to in a mining outer dewatering hose?
- 5.5 Is a more expensive mining hose always a better value?
The efficient management of water is a cornerstone of successful mining operations. From dewatering pits and tailings dams to managing slurry and process water, the equipment used must be robust, reliable, and specifically engineered for harsh conditions. At the heart of many of these critical dewatering systems is the Special Mining Outer Dewatering Hose. This comprehensive guide delves into the design, applications, and selection criteria for these specialized hoses, providing the in-depth knowledge needed to ensure operational efficiency and safety.
What is a Special Mining Outer Dewatering Hose?
Unlike standard hoses, a Special Mining Outer Dewatering Hose is a high-performance, heavy-duty tube designed to transport water, abrasive slurries, and tailings under high pressure and across challenging terrains. Its "special" designation comes from its construction, which is tailored to withstand the unique rigors of the mining environment, including abrasion, corrosion, crushing, and extreme weather conditions. These hoses are a critical component for maintaining dry working conditions, preventing environmental contamination, and ensuring the continuous flow of operations.
- Reinforcement: Typically features multiple layers of high-tensile steel or synthetic cord to handle high working pressures and vacuum conditions.
- Tube & Cover: Made from wear-resistant, anti-static rubber compounds that resist abrasion from suspended solids and degradation from sunlight, ozone, and chemicals.
- Flexibility: Engineered to remain flexible even in low temperatures, allowing for easier handling and deployment around a mine site.
Key Applications in the Mining Industry
The versatility of the mining dewatering hose makes it indispensable across various mining activities. Its primary function is to remove unwanted water, but its role extends to several high-stakes applications.
- Pit Dewatering: Pumping groundwater and rainwater from open-pit mines to maintain stable and accessible working floors.
- Tailings Management: Transporting fine-grained waste material mixed with water (tailings) from the processing plant to storage facilities.
- Slurry Transfer: Handling abrasive mixtures of solids and liquids during various mineral processing stages.
- Emergency Water Diversion: Rapidly deploying hose lines to control surface water runoff during heavy rainfall, preventing flooding.
High-Pressure Mining Dewatering Hose Specifications
When dealing with deep pits or long-distance pumping, pressure rating becomes a paramount concern. A high-pressure mining dewatering hose is constructed to withstand these intense forces without bulging, bursting, or collapsing. Understanding its specifications is crucial for system integrity and personnel safety.
- These hoses often have a minimum burst pressure rating several times higher than their working pressure.
- The wire reinforcement is spirally wound to provide exceptional strength while maintaining flexibility.
- They are tested to rigorous international standards to ensure performance under the most demanding conditions.
The following table compares key specifications for different classes of high-pressure dewatering hoses:
| Hose Class | Typical Working Pressure (PSI) | Reinforcement Type | Ideal Use Case |
| Standard Duty | 150 - 300 | Single Steel Wire | Shallow pits, low-head transfer |
| Heavy Duty | 300 - 600 | Double Steel Wire | Deep pit dewatering, medium-distance slurry |
| Extra Heavy Duty | 600+ | Multiple Spiral Steel Wire | High-head vertical lift, long-distance high-pressure transfer |
Abrasion-Resistant Slurry Discharge Hose Features
Slurries, by their nature, are highly abrasive and can quickly destroy a standard hose. An abrasion-resistant slurry discharge hose is specifically engineered to combat this wear, significantly extending service life and reducing downtime and replacement costs.
- Wear-Indicating Layers: Some hoses feature a colored inner layer that becomes visible when the top layer is worn, providing a clear visual cue for replacement before failure.
- Ultra-High Molecular Weight (UHMW) Liners: For extremely abrasive applications, special liners can be incorporated for superior wear resistance.
- Robust Cover: The external cover is also designed to resist cuts, gouges, and impact damage from being dragged over rough terrain.
How to Select the Right Dewatering Hose for Your Mine
Selecting the correct hose is not a one-size-fits-all process. A careful evaluation of your specific operational parameters is essential to ensure optimal performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness. Asking the right questions about how to choose a mining dewatering hose will guide you to the perfect solution.
- Material Compatibility: Identify the exact fluids or slurries the hose will carry, including their chemical composition, pH, and temperature.
- Pressure & Vacuum Requirements: Determine both the maximum working pressure and any potential vacuum conditions to prevent hose collapse.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider ambient temperature, exposure to UV light, ozone, and the presence of oils or chemicals.
- Application Logistics: Factor in the required length, bend radius, and the need for flexibility and weight for easy handling.
Heavy-Duty Outer Dewatering Hose Lifespan and Durability
Investing in a heavy-duty outer dewatering hose is a significant operational expense, and maximizing its lifespan is a key priority. Durability is a product of both initial quality and proper operational practices.
- Proper Storage: Store hoses in a cool, dry, dark place away from ozone sources (like electric motors) and in a relaxed, straight position, not kinked.
- Correct Installation: Avoid twisting the hose during installation and ensure it is not stretched or compressed beyond its design limits.
- Regular Inspection: Implement a routine inspection schedule to check for cover damage, wire rust, tube swelling, or any signs of wear.
Cost of Mining Grade Dewatering Hose Solutions
The cost of mining grade dewatering hose solutions is influenced by a wide array of factors. A cheaper initial price does not always equate to lower total cost of ownership. It's vital to consider the entire lifecycle cost.
- Material and Construction: Hoses with higher abrasion resistance, specialized rubber compounds, and complex reinforcement will cost more.
- Diameter and Length: Larger diameters and custom lengths directly impact the price.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Factor in the expected service life, frequency of replacement, and potential costs of downtime and cleanup from a hose failure.
The table below outlines the primary cost drivers for mining-grade hoses:
| Cost Factor | Impact on Price | Consideration for TCO |
| Hose Construction Complexity | High | A more expensive, durable hose may last 3x longer, offering better value. |
| Diameter & Length | Direct | Ensure the selected size matches flow rate requirements without being oversized. |
| Abrasion Resistance Rating | Medium to High | Critical for slurry applications; lower resistance leads to frequent, costly replacements. |
| Accessories (Couplings, Flanges) | Medium | Quality accessories are essential for a secure, leak-free connection. |
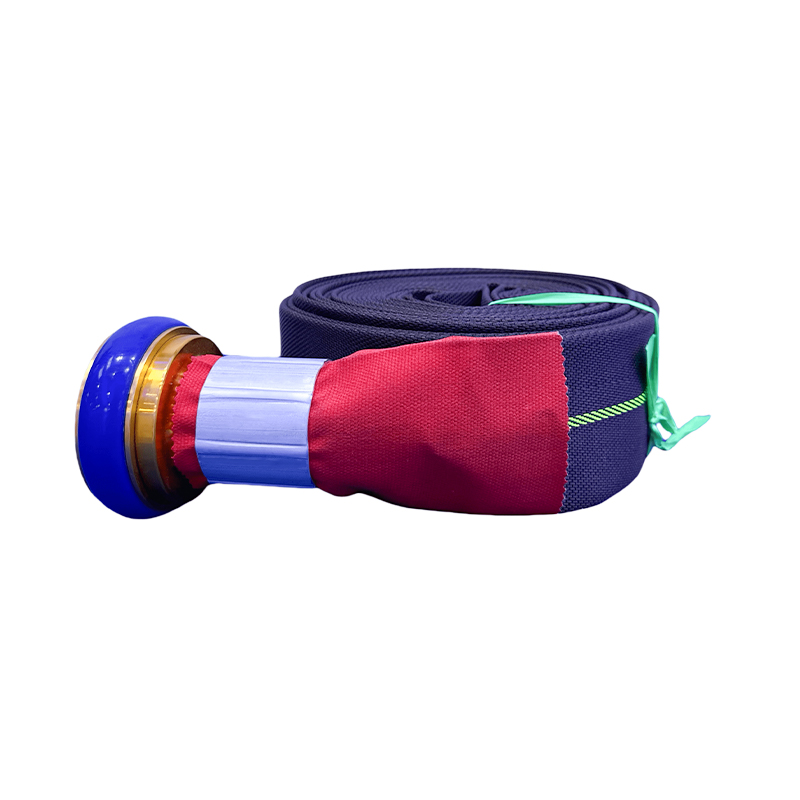
6-Inch Wear-Resistant Flat Hose With Storz Connector For Mining-Grade External Drainage
FAQ
What is the difference between a dewatering hose and a standard water hose?
The differences are substantial and critical for mining applications. A standard water hose is designed for low-pressure, clean water applications. In contrast, a Special Mining Outer Dewatering Hose is engineered for high-pressure, high-abrasion, and often high-vacuum conditions. It features a robust, wear-resistant tube, multiple layers of high-tensile steel wire reinforcement, and a thick, durable external cover to withstand being dragged over rough, rocky terrain. Using a standard hose in a mining environment would lead to rapid failure, posing significant safety and operational risks.
How often should a mining dewatering hose be inspected?
Inspection frequency should be risk-based. A visual inspection should be conducted before each use for obvious damage like cuts, bulges, or exposed reinforcement. A more formal, detailed inspection should be performed weekly or monthly, depending on the severity of the application. Key inspection points include checking for cover wear, signs of tube degradation (softening or cracking), coupling integrity, and any reduction in flexibility. For hoses used in high-pressure mining dewatering applications, adhering to a strict inspection schedule is non-negotiable for safety.
Can a mining dewatering hose handle acidic or chemical water?
This depends entirely on the hose's tube compound. While standard hoses may not be suitable, many heavy-duty outer dewatering hose models are available with specialized tube materials designed for chemical resistance. It is imperative to consult the hose manufacturer's chemical resistance chart, providing them with the exact chemical composition, concentration, and temperature of the fluid to be transported. Using a hose with inadequate chemical resistance can lead to premature tube failure, leaks, and hazardous spills.
What does the "outer" refer to in a mining outer dewatering hose?
The term "outer" primarily refers to the hose's external cover. This is the first line of defense against the external environment. In the context of a mining hose, the "outer" cover is specially compounded to resist weathering, ozone, UV radiation, abrasion from rocks and debris, and mechanical impact. A high-quality abrasion-resistant slurry discharge hose will have an outer cover that is just as tough as its inner tube, ensuring the internal reinforcement is protected from damage that could compromise the hose's pressure integrity.
Is a more expensive mining hose always a better value?
Not necessarily, but it often is. The key is to evaluate the cost of mining grade dewatering hose solutions based on Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). A cheaper hose may have a shorter lifespan, leading to more frequent replacements, increased downtime for swaps, and higher labor costs. A more expensive hose that is perfectly suited to the application—considering pressure, abrasion, and chemical factors—will typically last significantly longer, resulting in lower costs over time. The best value is the hose that delivers the required performance for the longest duration at the lowest TCO.


 en
en
 عربى
عربى