- 1 Defining the High-Temperature Threshold
- 2 The Material Challenge: High Heat vs. Low Temp
- 3 Ensuring Field Performance: Flexibility and Kink Resistance
- 4 Taizhou Jun'an Fire Technology: Commitment to Reliability
- 5 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 5.1 1. What is the typical Maximum safe working temperature for EPDM fire hose liners with hot water?
- 5.2 2. How does the choice of EPDM compounding affect the EPDM fire hose resistance to hot water and steam?
- 5.3 3. Why is Balancing high heat resistance and low temperature flexibility in hoses a challenge for materials scientists?
- 5.4 4. What is the primary purpose of Kink resistance testing for EPDM fire hose liners?
- 5.5 5. What role does EPDM rubber compounding for enhanced thermal aging play in long-term hose reliability?
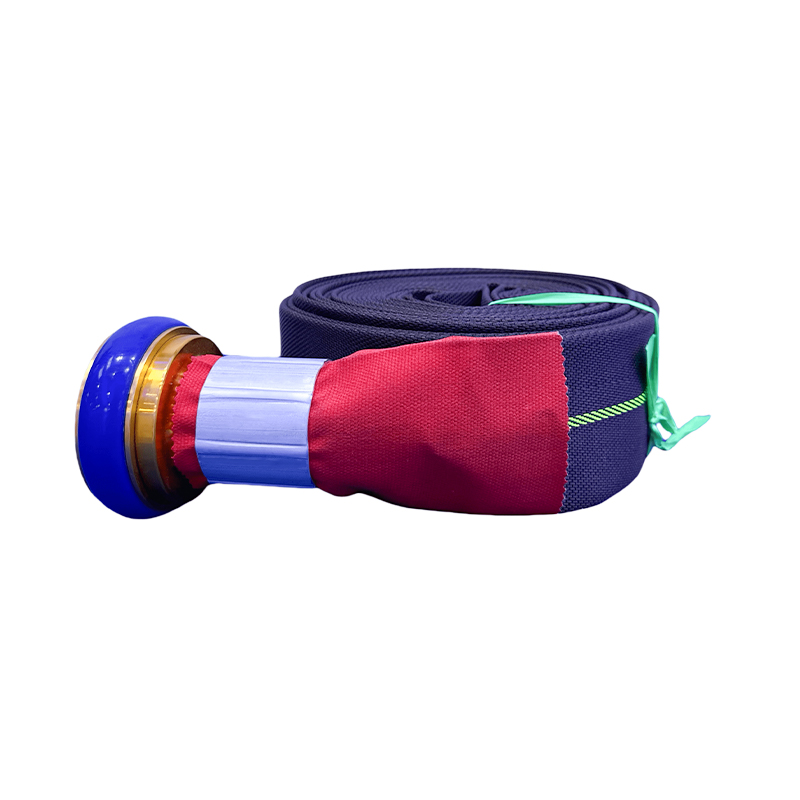
The modern **EPDM Fire Hose** is an engineering marvel, designed to handle both the intense thermal stresses of fire suppression and the mechanical demands of deployment in extreme climates. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) rubber is the material of choice for the inner liner due to its excellent resistance to heat, ozone, and chemicals. However, realizing the full potential of the hose requires precise technical control over the EPDM formulation to effectively meet the often-contradictory requirements of high-temperature stability and low-temperature flexibility.
EPDM Lined Hose Fiber Canvas Fire Extinguishing Flat Hose
Defining the High-Temperature Threshold
The primary function of the EPDM liner is to withstand the heat generated by the environment and the fluid passing through it.
Determining the Maximum safe working temperature for EPDM fire hose
- **Thermal Limit:** The safe operating limit is dictated by the thermal stability of the EPDM compound, which is usually significantly higher than that of PVC or standard natural rubber. High-grade **EPDM Fire Hose** liners typically maintain structural integrity and pressure ratings up to 150°C (302°F) for continuous service with water.
- **Safety Factor:** Determining the Maximum safe working temperature for EPDM fire hose involves setting a substantial safety margin below the material's decomposition temperature, ensuring the liner does not lose elasticity or degrade under stress during extended hot water exposure.
EPDM fire hose resistance to hot water and steam Hydrolysis
Unlike some other rubber polymers, EPDM exhibits superior EPDM fire hose resistance to hot water and steam hydrolysis. This is critical for industrial applications where steam tracing lines or very hot process water are involved. Prolonged exposure to high-temperature moisture can break down polymer chains; however, EPDM's chemically saturated backbone provides excellent stability against this degradation mechanism.
Liner Material Thermal Performance Comparison Table
| Liner Material Type | Typical Maximum Service Temperature (Water) | Relative Resistance to Thermal Aging |
|---|---|---|
| Standard PVC | Below 65°C (150°F) | Low (Prone to hardening) |
| High-Grade EPDM | Up to 150°C (302°F) | Excellent (Maintains elasticity) |
The Material Challenge: High Heat vs. Low Temp
A key technical challenge in rubber engineering is achieving high heat stability without sacrificing performance in cold weather.
Balancing high heat resistance and low temperature flexibility in hoses
- **Polymer Structure:** Rubber formulations designed for high thermal resistance often incorporate cross-linking agents and high filler loads that can raise the glass transition temperature (Tg). A higher Tg means the material stiffens and becomes brittle sooner in cold conditions.
- **Compounding:** Achieving the necessary **Balancing high heat resistance and low temperature flexibility in hoses** requires careful selection of low-Tg EPDM grades and appropriate plasticizers (though plasticizers must be thermally stable themselves) to keep the polymer chains mobile even at temperatures as low as -40°C (-40°F).
The Role of EPDM rubber compounding for enhanced thermal aging
The vulcanization system is paramount. Peroxide curing systems, compared to sulfur-based systems, generally produce stronger carbon-carbon cross-links in the EPDM polymer. This results in superior heat and compression set resistance, which is central to EPDM rubber compounding for enhanced thermal aging, allowing the liner to retain its mechanical properties (like elongation and tensile strength) after extended exposure to heat.
Ensuring Field Performance: Flexibility and Kink Resistance
The cold-weather flexibility of the **EPDM Fire Hose** directly relates to its usability and reliability during deployment.
Kink resistance testing for EPDM fire hose liners and Polymer Selection
- **Kink Resistance:** The resistance to kinking is a measure of the hose's ability to be bent sharply without collapsing its inner diameter, which would severely restrict water flow. This mechanical performance is verified through rigorous Kink resistance testing for EPDM fire hose liners often conducted at very low temperatures.
- **Flexural Modulus:** A low flexural modulus at low temperatures is desired, meaning the material remains soft and pliable for easy coiling and deployment. This is achieved through carefully optimized molecular weight distribution in the EPDM base polymer.
Impact of Polymer Molecular Weight on Flexural Modulus
Generally, EPDM polymers with a narrow molecular weight distribution are preferred as they allow for more consistent cross-linking and improved low-temperature elasticity. A high degree of polymer consistency helps ensure the hose can withstand the severe bending and twisting forces applied during field use without developing stress cracks.
Taizhou Jun'an Fire Technology: Commitment to Reliability
Taizhou Jun'an Fire Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in the production of high-quality fire hoses, fire equipment, and emergency rescue gear. Located near Shanghai, we employ modern, advanced production equipment and a team of senior technical and professional designers. Our focus is on engineering excellence in products like the rubber/PVC/PU lined fire hoses. We prioritize rigorous material selection and precise compounding to solve complex material challenges, such as the difficult task of Balancing high heat resistance and low temperature flexibility in hoses. Our technical expertise ensures that our **EPDM Fire Hose** products meet the demanding requirement for the Maximum safe working temperature for EPDM fire hose while passing critical Kink resistance testing for EPDM fire hose liners. We absorb the advantages of similar global products and offer reliable OEM and ODM services, dedicated to providing first-class equipment and high-quality service to domestic and foreign customers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the typical Maximum safe working temperature for EPDM fire hose liners with hot water?
High-grade EPDM fire hose liners are typically safe for continuous service with hot water up to approximately $150^\circ\text{C}$ ($302^\circ\text{F}$), significantly exceeding the limits of standard rubber or PVC liners.
2. How does the choice of EPDM compounding affect the EPDM fire hose resistance to hot water and steam?
Using peroxide curing systems and chemically stable EPDM grades minimizes the risk of polymer hydrolysis and oxidation, thereby enhancing the hose's resistance to steam and hot water aging compared to less stable, sulfur-cured compounds.
3. Why is Balancing high heat resistance and low temperature flexibility in hoses a challenge for materials scientists?
Materials that are chemically modified for high heat resistance often become stiffer, which raises their glass transition temperature (Tg). This makes them prone to hardening and embrittlement at cold temperatures, making the balance a critical engineering trade-off.
4. What is the primary purpose of Kink resistance testing for EPDM fire hose liners?
The primary purpose is to ensure that the hose maintains its full inner diameter and does not restrict water flow even when bent sharply during deployment in cold or challenging field conditions.</HED
5. What role does EPDM rubber compounding for enhanced thermal aging play in long-term hose reliability?
Proper compounding ensures that the hose liner retains essential mechanical properties—such as elasticity, tensile strength, and burst pressure—over years of use, even after repeated exposure to heat and UV radiation.</HED


 en
en
 عربى
عربى